UTI Symptoms & Treatment : Best 3 Medicines
UTI Symptoms & Treatment is the topic of today’s discussion with that we discuss Best 3 Medicines, we also learn diagnosis of UTI in men, women & kids.
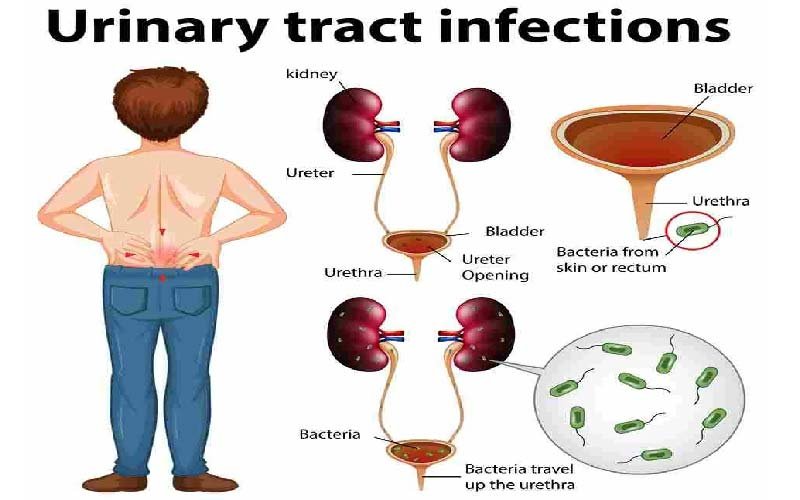
A urinary tract infection (UTI), otherwise called intense cystitis or bladder contamination, is an irresistible condition influencing the urinary lot. At the point when it basically includes the lower urinary plot, it is named straightforward cystitis (bladder contamination), and in the event that it influences the upper urinary parcel, it’s alluded to as pyelonephritis (kidney disease).
Side effects of a lower urinary parcel contamination might incorporate excruciating pee, regular pee, and an earnest need to pee. Pyelonephritis might give fever and flank torment notwithstanding lower UTI side effects. In older and youthful people, side effects can be dubious or vague. The essential causative specialist for the two kinds of UTIs is Escherichia coli, albeit different microorganisms like microbes, infections, or parasites may sometimes be dependable.
Urinary lot contaminations are more normal in ladies than in men, with roughly 50% of all ladies encountering no less than one UTI in the course of their life. Repeats are regular, and take a chance with factors incorporate female life systems, sex, and a family background of UTIs. Pyelonephritis frequently follows a bladder disease however can likewise result from a circulation system contamination.
In youthful, sound ladies, conclusion is many times in view of side effects alone. Notwithstanding, in cases with obscure or abnormal side effects, diagnosing UTIs can challenge, as microorganisms might be available without an unmistakable disease. For complex cases or when starting treatment falls flat, a pee culture might be essential. In instances of successive contaminations, low-portion anti-microbials might be recommended as a preventive measure.
Simple UTIs can regularly be treated with a short course of anti-toxins. Nonetheless, anti-toxin opposition is a developing concern. Convoluted cases might require longer or intravenous anti-toxin treatment, and in the event that there’s no improvement inside a couple of days, further demonstrative testing becomes essential. UTIs are the most widely recognized bacterial diseases in ladies, with roughly 10% encountering UTIs every year. In situations where microorganisms or white platelets are tracked down in the pee yet there are no side effects, anti-microbials are by and large not suggested, with the exception of pregnant ladies.
Diagnosis
In direct cases, a determination might be made and treatment gave in light of side effects alone minus any additional lab affirmation. Notwithstanding, in muddled or unsure cases, it could be useful to affirm the analysis through urinalysis, which searches for urinary nitrites, white platelets (leukocytes), or leukocyte esterase. Pee microscopy checks for the presence of red platelets, white platelets, or microbes.
A pee culture is viewed as certain when it shows a bacterial province count of ≥10^3 settlement framing units per mL of an ordinary urinary plot creature. Anti-toxin responsiveness can not entirely set in stone through these societies, helping with the choice of suitable treatment. In any case, a few ladies with negative societies might in any case improve with anti-toxin treatment. Given the obscure idea of side effects and the shortfall of dependable tests for UTIs, conclusion can be trying in the old.
Classification:
UTIs can include either the lower or upper urinary plot. In the lower parcel, it’s known as a bladder disease (cystitis), while in the upper lot, it’s known as kidney contamination (pyelonephritis). Asymptomatic bacteriuria is a condition where the pee contains critical microbes, however there are no side effects of contamination. UTIs including the upper plot in people with diabetes mellitus, during pregnancy, in guys, or in immunocompromised people are viewed as confounded. In sound, premenopausal ladies, it is viewed as straightforward. At the point when UTIs in kids are related with fever, they are considered to be upper urinary plot diseases.
Diagnosis in Children
Diagnosing UTIs in kids requires a positive urinary culture. The technique for assortment can prompt tainting difficulties, with various end values for “clean-get” mid-stream tests, catheter-got examples, and suprapubic desires. Renal ultrasound and voiding cystoure throgram are suggested in youngsters under two years of age who’ve had a UTI, particularly on the off chance that strange discoveries are available.

Differential Diagnosis:
In ladies with cervicitis, vaginitis, or young fellows with UTI-like side effects, Chlamydia trachomatis or Neisseria gonorrheae contaminations could be dependable. Vaginitis may likewise result from a yeast disease. Interstitial cystitis, portrayed by ongoing bladder torment, might be viewed as in cases with different UTI-like episodes yet bad pee societies that don’t answer anti-infection agents. Prostatitis is one more condition to think about in the differential conclusion.
UTI Symptoms and Signs
Lower urinary plot contamination (bladder disease) is portrayed by normal side effects like difficult pee, regular pee, and a pressing need to pee. Certain individuals might encounter gentle to serious uneasiness, including torment over the pubic bone or lower back. Upper urinary plot contaminations (pyelonephritis) can give flank torment, fever, sickness, retching, and the exemplary side effects of lower urinary parcel contamination. Hematuria (horrendous pee) or pyuria (discharge in the pee) can once in a while be noticed.
- Children:
In small kids, a UTI might give fever as the essential side effect. In babies, extra signs can incorporate taking care of challenges, regurgitating, expanded rest, and jaundice. More seasoned kids might foster new-beginning urinary incontinence.
- Elderly:
UTI side effects in the older might dubious or need, with introductions like incontinence, changed mental status, exhaustion, or even sepsis. Previous incontinence or dementia can additionally confuse finding.
- UTI Symptoms Cause:
The most widely recognized causative specialist for UTIs is Escherichia coli (E. coli), representing 80-85% of cases, while Staphylococcus saprophyticus is answerable for 5-10%. Once in a while, UTIs can result from viral or parasitic diseases, with other remarkable bacterial causes including Klebsiella, Proteus, Pseudomonas, Enterococcus, and Enterobacter. UTIs brought about by Staphylococcus aureus are ordinarily auxiliary to blood-borne diseases.
- UTI symptoms after Sex
In physically dynamic young ladies, sexual action adds to 75-90% of bladder diseases, with the gamble associated with the recurrence of sexual action. Post-menopausal ladies experience no adjustment of the gamble of UTIs connected with sexual movement. Spermicide use, paying little heed to sexual recurrence, builds UTI risk. Ladies are more inclined to UTIs than men because of contrasts in life structures, with the female urethra being more limited and nearer to the butt. Post-menopausal ladies are at an expanded gamble of UTIs because of diminished estrogen levels, which brings about a deficiency of defensive vaginal greenery.
- UTI Symptoms after Urinary Catheters:
The utilization of urinary catheters builds the gamble of UTIs, with the gamble of bacteriuria between 3-6% each day. Prophylactic anti-toxins are inadequate in diminishing suggestive contaminations.
- Others:
A genetic predisposition to bladder infections may run in families. Other risk factors include diabetes, being uncircumcised, and having an enlarged prostate. Various anatomical, functional, or metabolic abnormalities can complicate UTIs. In children, UTIs are associated with vesicoureteral reflux (abnormal urine flow from the bladder to the kidneys) and constipation. Persons with spinal cord injuries are at an increased risk for UTIs due to chronic catheter use and voiding dysfunction. Cranberry juice or supplements do not appear to be effective in preventing or treating UTIs in this population.
UTI in Pregnancy
UTIs are more concerning during pregnancy due to the increased risk of kidney infections. High progesterone levels during pregnancy elevate the risk of decreased muscle tone in the ureters and bladder, leading to a greater likelihood of urine reflux. While pregnant women do not have an increased risk of asymptomatic bacteriuria, if bacteriuria is present, they have a 25-40% risk of kidney infection. Consequently, treatment is recommended if urine testing reveals signs of infection, even in the absence of symptoms. Safe antibiotics like cephalexin or nitrofurantoin are commonly used. A kidney infection during pregnancy can lead to premature birth or pre-eclampsia, a condition characterized by high blood pressure and kidney dysfunction during pregnancy that can result in seizures.
UTI Treatment
- Fluoroquinolones are not suggested as the first-line treatment because of worries about anti-microbial obstruction. Amoxicillin-clavulanate shows up less successful than different choices. Opposition has created to different anti-microbials because of their inescapable use. Trimethoprim alone is viewed as comparable to trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole in certain nations. For straightforward UTIs in kids, a three-day course of anti-infection agents is frequently adequate. Repetitive UTIs in ladies might profit from self-therapy upon side effect repeat, with clinical subsequent provided that underlying treatment comes up short.
- Convoluted UTIs require greater assessment, treatment, and follow-up. It is fundamental to Distinguish and tending to hidden intricacies. Expanding anti-toxin obstruction presents worries for the treatment of muddled and repetitive UTIs.
- Pyelonephritis is dealt with more forcefully than straightforward bladder diseases, utilizing either a more extended course of oral anti-toxins or intravenous anti-toxins. The decision of anti-toxin and span of treatment might rely upon nearby obstruction rates. Extreme cases might require medical clinic confirmation, particularly in the event that urinary check from a kidney stone is thought.
UTI Medication
For individuals with recurrent UTIs, a prolonged course of daily antibiotics is effective. Commonly used medications include nitrofurantoin, trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, and methenamine. In cases linked to intercourse, post-coital antibiotics may be beneficial. In post-menopausal women, topical vaginal estrogen may reduce recurrence. Antibiotics following short-term urinary catheterization decrease the subsequent risk of a bladder infection. Several vaccines are under development.
- UTI Medications in Children:
The evidence for prophylactic antibiotics reducing UTIs in children is weak. Recurrent UTIs are a rare cause of kidney problems if there are no underlying kidney abnormalities, accounting for less than 0.33% of chronic kidney disease cases in adults. As of 2011, the impact of routine circumcision on preventing UTIs has not been well studied.
- Alternative Medicine:
Some research suggests that cranberry products may reduce the frequency of UTIs in individuals with recurrent infections, although the benefit is small, and long-term tolerance may be an issue. As of 2011, intravaginal probiotics require further study to determine their efficacy.
Epidemiology
UTIs are the most well-known bacterial contaminations in ladies, with around 10% encountering UTIs every year. Repeats are normal, with almost 50% of those impacted encountering a second contamination soon. UTIs happen more habitually in females than guys, with pyelonephritis being more uncommon. UTIs are a main source of emergency clinic obtained contaminations, representing around 40% of such cases. Asymptomatic bacteriuria is more normal in old ladies and men north of 75. It’s seen in 2% to 10% of pregnancies.
Prevention
Several measures have not been conclusively shown to affect the frequency of UTIs. These include urinating immediately after intercourse, the type of underwear used, personal hygiene practices after urinating or defecating, bathing or showering habits, holding one’s urine, tampon use, and douching. For those with frequent UTIs using spermicide or a diaphragm for contraception, alternative methods are recommended. Condom use without spermicide or birth control pills does not increase the risk of uncomplicated UTIs. In men with benign prostatic hyperplasia, urinating in a sitting position can improve bladder emptying and potentially reduce UTI risk.
Society and Culture:
In the United States, UTIs result in numerous office visits, emergency department visits, and hospitalizations each year, incurring significant costs related to medical care and lost work time. The direct cost of treatment in the United States is estimated at $1.6 billion annually.
Pathogenesis:
The bacteria that cause UTIs typically enter the bladder through the urethra, with potential infection routes via the blood or lymph. Fecal transmission to the urethra is believed to be a common source of infection, with females at higher risk due to their anatomical differences. Once in the bladder, E. coli can attach to the bladder wall and form a biofilm that resists the body’s immune response.
Conclusion
ICD-10 codes for UTIs (including lower and upper tract infections) include N30.0 (Acute cystitis), N10 (Acute tubulo-interstitial nephritis), and N12 (Tubulo-interstitial nephritis, not specified as acute or chronic). Please note that the ICD-10 coding can be more specific and detailed in clinical practice, accounting for factors such as the causative agent and any associated complications