varicose veins symptoms and treatment
varicose veins symptoms and treatment is a query of most of cardiac patients, so to start with its pathology and symptoms,
Pathology and Symptoms
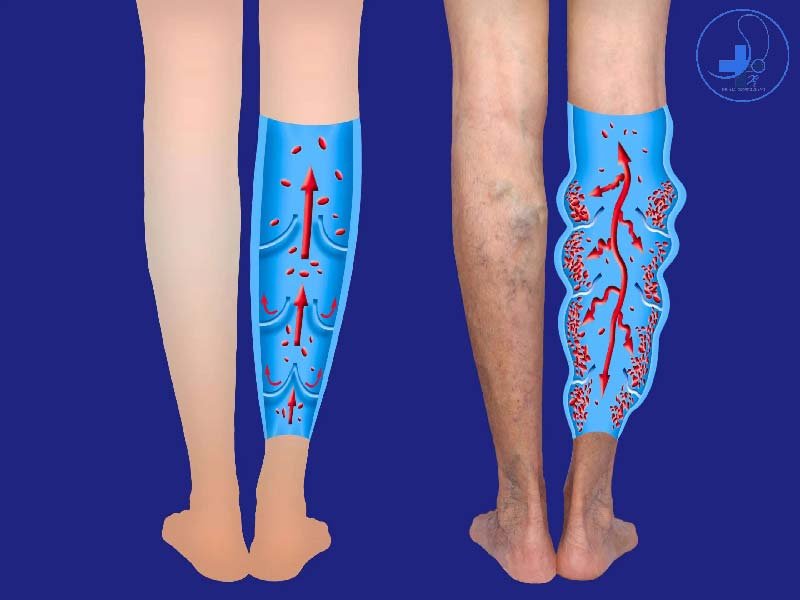
Varicose veins are a condition characterized by enlargement and twisting of veins, generally happening in the legs, although they can show somewhere else in the body. These veins commonly have leaflet valves that prevent the backward flow of blood (retrograde flow or reflux). The contraction of leg muscles supports in pumping blood back to the heart, balancing the impacts of gravity. However, when veins become varicose, the valve leaflet fails to meet accurately. This condition allows blood to flow in reverse, making the veins enlarge further. Varicose veins primarily effect the superficial veins of the legs, which are under high compression while standing. Past superficial worries, varicose veins can be painful, especially while standing for extended periods. In serious cases, they can result in leg swelling, venous dermatitis (eczema), skin thickening (lipodermatosclerosis), and ulceration. Althpough life threatning complications are rare, varicose veins can sometime be confused with deep vein thrombosis, a possibly hazardous condition.
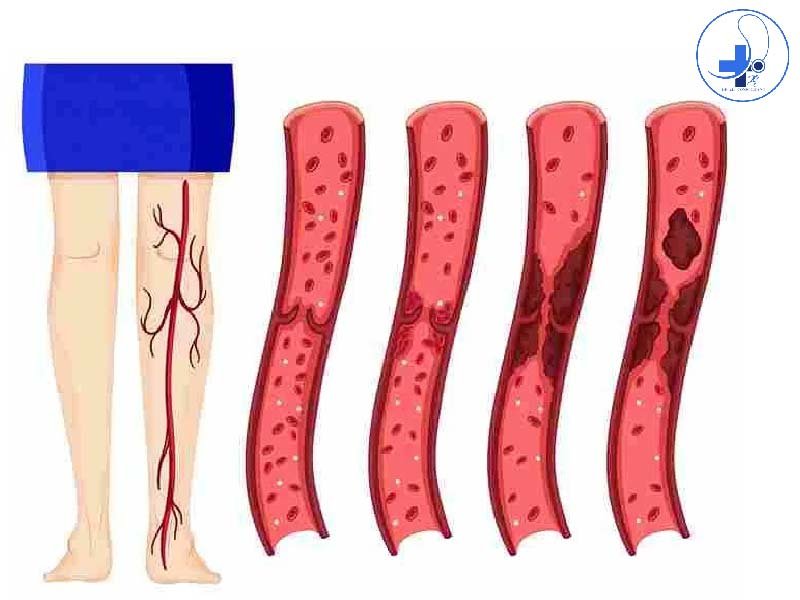
Causes: What are reasons for varicose vein
Varicose veins are more normal in women than in men and are often connected with a family background of the condition. Other factors that can contribute to their development include pregnancy, obesity, menopause, aging, prolonged standing, leg injuries, and straining of the abdominal area. In opposition to poipular belief, crossing the legs or ankles is unlikely to be a direct cause of varicose veins. At times, varicose veins might be related with conditions, for example, post-phlebitic obstruction or incontinence, venous and arteriovenous abnormalities. Hyperhomocysteinemia, a condition described by raised levels of homocysteine in the body, can also play an important role in the development of varicose veins. Homocysteine can harm and repress the development of key structural components of arteries, including collagen, elastin, and proteoglycans. This degradation effects the function and structure of these proteins, ultimately affecting the health of veins. Varicose veins might also occur as a result of hyperhomocysteinemia’s corrosive effects on long-lived proteins like collagen and elastin, or lifelong proteins like fibrillin. While the drawn out impacts of hyperhomocysteinemia on veins are trying to establish through clinical trials, it’s a significant thought with regards to varicose veins.
Treatment: What are treatment options for varicose vein
Conservative:
Symptoms of varicose veins can be managed through different conservative measures:
- Elevating the Legs: Frequent leg rise can provide temporary from symptoms.
- Exercise: While Excercise is often suggested, evidence in supporting its effectiveness in treating varicose veins is limited.
- Compression Stockings: Graduated compression stockings with variable compression gradient (Class II or III) can decrease swelling, improve nutritional exchange, and improve microcirculation in effected legs. They additionally provide relief from distress. However, they should be used surgically in patients with simultaneous blood vessel sickness.
- Intermittent Pneumatic Compression Devices: These devices can lessen swelling and improve circulation.
- Medications: Diosmin/Hesperidine and different flavonoids might be utilized.
- Anti-inflammatory Medications: In case of superficial thrombophlebitis, anti-inflammatory drugs like ibuprofen or headache medicine might be recommended alongside graduated compression hosiery. however, there is a risk of gastrointestinal bleeding with these medications. Broad thrombophlebitis could require anticoagulation, thrombectomy, or sclerotherapy of involved vein.
- Topical Gel Application: Effective gels can assist with managing symptoms connected with varicose veins, including irritation, pain, swelling, itching, and dryness. This painless methodology often brings about great patient consistence.
Active:
- Surgical:
A few surgical procedures have been utilized for treating varicose veins:
- Vein Stripping: This customary strategy includes eliminating all or part of the saphenous vein (incredible or lesser) main trunk. Complexities can include deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, and wound infections. There is proof that the great saphenous vein can include deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, and wound infections. Moreover, the removal of saphenous main trunks during stripping renders them inaccessible for use as venous bypass grafts in future surgeries, such as those required for coronary or leg artery disease.
- Other Surgical Treatments: Elective surgical methodologies incorporate wandering phlebectomy, vein ligation, and cryosurgery. Cryosurgery includes freezing the vein with a cryoprobe, which can be a choice to stay away from a distal cut for stripper removal.
Non-surgical:
- Sclerotherapy: This non-surgical treatment includes injecting a sclerosant (medication) into the veins to make them shrink. Common sclerosants includes polidocanol, sodium tetradecyl sulfate, hypertonic saline, glycerin, and chromated glycerin. Froth sclerosants can also be utilized to treat larger varicose veins under ultrasound direction. This technique is successful for spider veins and varicose veins that endure or repeat after vein stripping. Difficulties are rare yet can incorporate blood clots, ulceration, and, in very intriguing cases, anaphylactic responses.
- Endovenous Warm Ablation (ELA) and Radiofrequency Ablation (ERA): ELA and Period are less intrusive method used to treat varicose veins. ELA utilizes laser energy, while ERA uses radiofrequency energy to seal the main spilling vein. These methods are proceeded as short term treatments without the requirement for general anesthesia. Complications can include burns, paraesthesia, and slightly higher rates of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism compared to traditional surgery.
Ultrasound-Guided Foam Sclerotherapy: Foam sclerotherapy can be performed under ultrasound guidance to treat larger varicose veins, including the great saphenous and small saphenous veins.
Investigations
All patients with varicose veins should undergo through Duplex doppler ultrasound examining for examination. This approach has been displayed to reduce repeat rates and reoperation rates over time.

Complications:
While varicose veins are usually harmless, severe cases can lead to complications due to impaired circulation:
Pain, tenderness, heaviness, and limited mobility, hindering daily activities.
Skin conditions, such as dermatitis, due to waste product buildup in the leg.
Skin ulcers, often near the ankle, known as venous ulcers.
Carcinoma or sarcoma can develop in long-standing venous ulcers, though this is relatively rare.
Severe bleeding from minor trauma, particularly concerning in elderly individuals.
Blood clotting within affected veins, leading to superficial thrombophlebitis, which can extend into deep veins.
Acute fat necrosis, especially at the ankle of overweight patients with varicose veins, with a higher prevalence in females.
Stages of varicose veins range from C0 (no visible signs) to C6 (skin changes with active ulcers).
Varicose Veins ICD 10
The ICD-10 code for varicose veins is I83. The full code for varicose veins is I83, followed by a specific subcode to further define the condition. For example, I83.90 is the subcode for unspecified varicose veins of the lower extremities. The specific subcode may vary depending on the location, severity, and other factors related to the varicose veins. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for a precise diagnosis and the appropriate ICD-10 code.
Conclusion
In conclusion, varicose veins are a typical vascular condition with different treatment choices. Moderate measures, surgeries, and non-surgical treatments, for example, sclerotherapy, endovenous thermal ablation, and ultrasound-guided foam sclerotherapy are accessible, depending upon the seriousness of the condition and individual patient factors. Early diagnosis and appropriate intervention can help alleviate symptoms and prevent complications associated with varicose veins